a. Plane scale
Plain scale are used to read our measure length up to two units or unit and its one sub division such as centimeter(cm) and millimeter(mm). It can measure length upto first decimal (eg. 2.5cm). It consists of a line divided into number of equal main part and the first main part is subdivided into smaller parts.
b. Diagonal scale
Diagonal scales are used to read or measure length up to three units (for example, decimeter(dm) centimeter(cm) and millimeters(mm)). It can measure length upto second decimal (eg. 2.54dm).

c. Scale of chord
A scale of chord may be used to set or read an angle in the absence of a protractor. The constructions are based on the length of chord of angle measured on the same arc.
d.Vernier scale
A vernier scale is used to measure three consecutive units of a metric scale. It can measure length up to second decimal (eg. 3.45 dm). Its accuracy in measurement is equivalent to that of diagonal scale. It consists of two parts: a. Main scale and b. Vernier scale
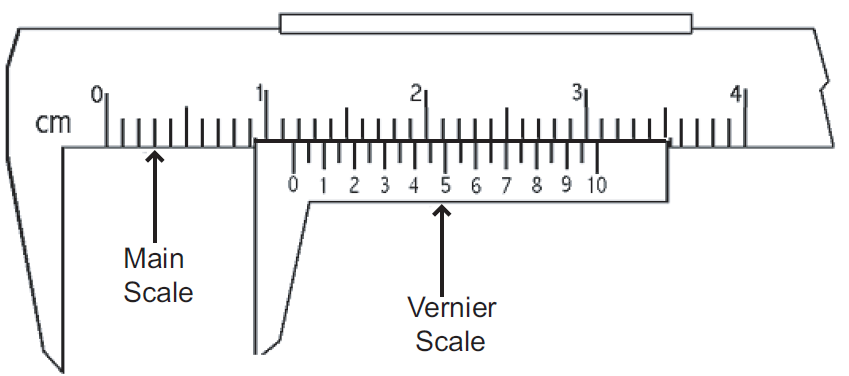
Vernier scale are of two types
i. Direct vernier scale (Forward vernier scale)
- Smallest division of main scale > Smallest division of vernier scale
- Least count = smallest division of main scale – smallest division of vernier scale
ii. Retrograde vernier scale (Backward vernier scale)
- Smallest division of main scale < Smallest division of vernier scale
- Least count = smallest division on vernier scale – smallest division on main scale
